Pets and Parasites: Understanding Single-Celled Parasites
We often associate the word parasite with fleas, ticks and lice. However, there are also a number of far smaller parasites that can infect our pets. Have you ever heard of single-celled parasites? They’re far more common than you might think.
The kingdom protozoa: single-celled parasites
Protozoa are microscopic organisms that are made up of just a single cell. In many cases, these protozoa are parasitic, entering the bodies of more complex organisms and using these hosts to survive. The following protozoa are fairly common in domestic animals:
Leishmania
This parasite causes leishmaniasis, which mainly affects mammals and reptiles. Sandflies and mosquitoes act as vectors for the disease, passing it from one animal to the next. Mosquitoes ingest the protozoa when feeding on an infected animal, before going on to infect another, previously healthy animal, the next time they feed.
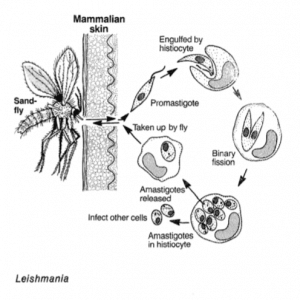
There are three different types of leishmaniasis: some affect the skin and mucus, while others affect the gut. Visceral leishmaniasis causes enlargement of the spleen, a symptom which vets can use to help them diagnose the disease.
Trypanosoma
Trypanosome brucei and T. cruzi are the parasites which cause trypanosomiasis, or sleeping sickness. The tsetse fly is the main vector for the disease, ingesting the protozoal larvae while feeding on an infected animal and passing it on to the next host. The larvae enter the new organism through small wounds in the skin, moving through the bloodstream until they reach the heart muscles.
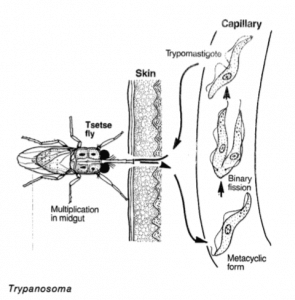
On the other hand, we have Trypanosoma evansi, which causes the disease known as “surra”. It affects horses, camels, ox, and buffalo, causing generalized edema and severe weight-loss.
Giardia and Trichomonas: single-celled flagellated parasites
Most of these protozoa form part of the gut flora in animals. Some also live in the gills or urogenital tracts of fish, often in the form of harmful cysts.
Sometimes, however, these protozoa act as parasites, as is the case with Giardia. This is the most common type of flagellated protozoa in birds and mammals, and lives in the walls of the intestine. Trichomonas is another example of this type of parasite, and often affects domestic pets.
Histomonas
Histomonas meleagridis mainly affects poultry. This single-celled parasite causes histomoniasis, which is transmitted orally when a bird comes into contact with infected feces.
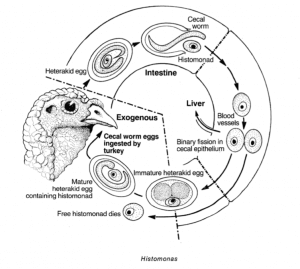
Once in the intestines, the larvae emerge, invading the intestinal wall, and even reaching the liver.
Amoeba
Amoeba are protozoa which can be both free-living and parasitic. The most common parasitic amoeba are Entamoeba, which are transmitted when an animal comes into contact with the feces of an infected animal. The feces contain cysts which, when ingested, release trophozoites into the intestine. In some cases, they may even spread to nearby organs.
Entamoeba histolytica is found in dogs, cats and humans, while E. invadans is found in reptiles.
Myxozoa
While these parasites have been found in a number of cold-blooded animals, very little is known about their life cycle. What we do know is that they are normally ingested in food or drinking water. On reaching the stomach, they pass through the stomach wall to reach the bloodstream and, from there, begin to infect other tissues.
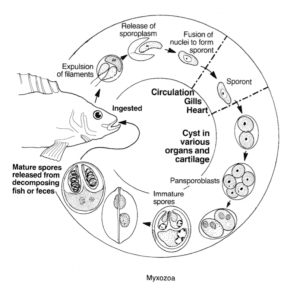
Myxozoa can cause serious diseases in fish, and has a huge impact on the fishing industry.
Ciliated single-celled parasites
Many ciliated parasites are found in the digestive tracts of domestic animals, which ingest the parasites through food or drinking water. Once inside the body, they release trophozoites into the gut and begin to multiply. They later pass out of the body in the feces.
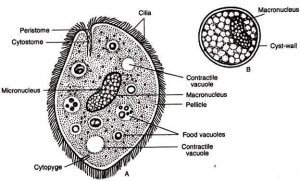
One of the most common species is Balantidium coli, which affects pigs, rodents and primates.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Protozoo [Internet]. Es.wikipedia.org. 2019 [cited 17 September 2019]. Available from: https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protozoo
- Gardiner C, Fayer R, Dubey J. An atlas of protozoan parasites in animal tissues. Washington: United States Department of Agriculture; 1988.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.